If the distance 's' travelled by a body in time 't' is given by then the acceleration equals
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
The velocity of a particle moving on the x-axis is given by where v is in m/s and x is in m. Find its acceleration in when passing through the point x=2m.
1. 0
2. 5
3. 11
4. 30
A particle moves in the XY plane and at time t is at the point whose coordinates are . Then at what instant of time, will its velocity and acceleration vectors be perpendicular to each other?
(1) 1/3 sec
(2) 2/3 sec
(3) 3/2 sec
(4) never
A particle is moving along positive x-axis. Its position varies as , where x is in meters and t is in seconds.
Initial acceleration of the particle is
(A) Zero
(B)
(C)
(D)
Two forces and are acting on a particle.
The resultant force acting on particle is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
and , then angle between vectors A and B is:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
If a curve is governed by the equation y = sinx, then the area enclosed by the curve and x-axis between x = 0 and x = is (shaded region):

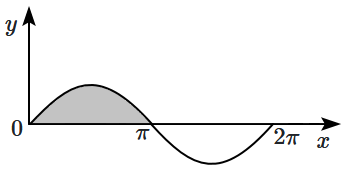
1. \(1\) unit
2. \(2\) units
3. \(3\) units
4. \(4\) units
The acceleration of a particle starting from rest varies with time according to relation, . The velocity of the particle at time instant \(t\) is: \(\left(\text{Here,}~ a=\frac{dv}{dt}\right)\)
1.
2.
3.
4.
The displacement of the particle is zero at \(t=0\) and at \(t=t\) it is \(x\). It starts moving in the \(x\)-direction with a velocity that varies as \(v = k \sqrt{x}\), where \(k\) is constant. The velocity will: (Here, \(v=\frac{dx}{dt}\))
| 1. | vary with time. |
| 2. | be independent of time. |
| 3. | be inversely proportional to time. |
| 4. | be inversely proportional to acceleration. |
The acceleration of a particle is given as \(a= 3x^2\).
At \(t=0,v=0\) and \(x=0\). It can then be concluded that the velocity at \(t=2~\text{s}\) will be: (Here, \(a=v\frac{dv}{dx}\))
1. \(0.05~\text{m/s}\)
2. \(0.5~\text{m/s}\)
3. \(5~\text{m/s}\)
4. \(50~\text{m/s}\)
