A particle is moving along positive x-axis. Its position varies as , where x is in meters and t is in seconds.
Initial acceleration of the particle is
(A) Zero
(B)
(C)
(D)
Two forces and are acting on a particle.
The resultant force acting on particle is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
and , then angle between vectors A and B is:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
If a curve is governed by the equation y = sinx, then the area enclosed by the curve and x-axis between x = 0 and x = is (shaded region):

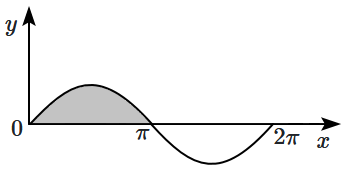
1. \(1\) unit
2. \(2\) units
3. \(3\) units
4. \(4\) units
The acceleration of a particle starting from rest varies with time according to relation, . The velocity of the particle at time instant \(t\) is: \(\left(\text{Here,}~ a=\frac{dv}{dt}\right)\)
1.
2.
3.
4.
The displacement of the particle is zero at \(t=0\) and at \(t=t\) it is \(x\). It starts moving in the \(x\)-direction with a velocity that varies as \(v = k \sqrt{x}\), where \(k\) is constant. The velocity will: (Here, \(v=\frac{dx}{dt}\))
| 1. | vary with time. |
| 2. | be independent of time. |
| 3. | be inversely proportional to time. |
| 4. | be inversely proportional to acceleration. |
The acceleration of a particle is given as \(a= 3x^2\).
At \(t=0,v=0\) and \(x=0\). It can then be concluded that the velocity at \(t=2~\text{s}\) will be: (Here, \(a=v\frac{dv}{dx}\))
1. \(0.05~\text{m/s}\)
2. \(0.5~\text{m/s}\)
3. \(5~\text{m/s}\)
4. \(50~\text{m/s}\)
The acceleration of a particle is given by \(a=3t\) at \(t=0\), \(v=0\), \(x=0\). The velocity and displacement at \(t = 2~\text{sec}\) will be:
\(\left(\text{Here,} ~a=\frac{dv}{dt}~ \text{and}~v=\frac{dx}{dt}\right)\)
1. \(6~\text{m/s}, 4~\text{m}\)
2. \(4~\text{m/s}, 6~\text{m}\)
3. \(3~\text{m/s}, 2~\text{m}\)
4. \(2~\text{m/s}, 3~\text{m}\)
The 9 kg block is moving to the right with a velocity of 0.6 m/s on a horizontal surface when a force F, whose time variation is shown in the graph, is applied to it at time t = 0. Calculate the velocity v of the block when t= 0.4s. The coefficient of kinetic fricton is . [This question includes concepts from Work, Energy & Power chapter]
1. 0.6 m/s
2. 1.2 m/s
3. 1.8 m/s
4. 2.4 m/s
The relationship between force and position is shown in the figure given (in one dimensional case). Find the work done by the force in displaying a body from x= 1 cm to x= 5cm is [This question includes concepts from Work, Energy and Power chapter]
1. 10 erg
2. 20 erg
3. 30 erg
4. 40 erg


