All the following are examples of Mendelian disorders except:
1. Hemophilia
2. Sickle cell anemia
3. Phenylketonuria
4. Down's syndrome
The pure line round seeded pea plant was crossed with wrinkled seeded pea plant. The F1 generation is ____ and it can be explained by _____. (respectively)
1. Wrinkled : Law of segregation
2. Round : law of dominance
3. Round : Condominance
4. Wrinkled : Law of dominance
A man suffering from haemophilia marries a normal woman without any history of haemophilia in her family. What percentage of their sons are affected?
1. 100%
2. 75%
3. 50%
4. 0%
Study the given pedigree chart and choose the correct statement
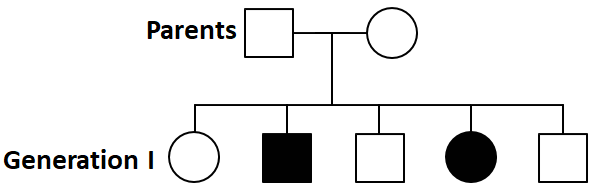
| 1. | The trait under study is dominant. |
| 2. | Both parents are homozygous. |
| 3. | The trait can be X-linked recessive disease haemophilia. |
| 4. | The trait depicted is autosomal recessive like cystic fibrosis. |
progeny resemble both the parents in the case of:
1. Complete dominance
2. Incomplete dominance
3. Codominance
4. Multiple allelism
Which of the following traits in the garden pea plant would express itself only in homozygous condition?
1. Violet flower color
2. Terminal flower position
3. Green pod color
4. Yellow seed color
How many of the following statements are correct?
| 1 | Phenyl ketonuria leads to mental retardness. |
| 2 | Thalassemia is quantitative where as sickle-cell anaemia is qualitative. |
| 3 | Possibility of female becoming haemophilic is extramely rare. |
| 4 | 8% of male & 0.4% of females are haemophilic. |
Options
1. All
2. 3
3. 2
4. 1
Find incorrect match
1. Polygenic inheritance – Spread across of gradient.
2. Pleiotropy – Single gene multiple phenotype.
3. X body of henking – One each in sperm.
4. Pedigree analysis – Mendelian trait.
How many type(s) of gametes is/are produced by a double recessive parent?
1. One
2. Two
3. Four
4. Six
The number of linkage groups in pea is
1. 14
2. 7
3. 9
4. 24
