Physics - Section A
1. Let \(r\) be the distance of a point on the axis of a magnetic dipole from its centre. The magnetic field at such a point is proportional to:
1. \(\dfrac 1 r\)
2. \(\dfrac 1 {r^2}\)
3. \(\dfrac 1 {r^3}\)
4. none of these
2. An electric dipole is placed at an angle of
\(30^\circ\) with an electric field intensity
\(2\times10^5~ \text{N/C}\). It experiences a torque equal to
\(4~\text{N-m}\). The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is
\(2~ \text{cm}\), is:
| 1. |
\(8~\text{mC}\) |
2. |
\(2~\text{mC}\) |
| 3. |
\(5~\text{mC}\) |
4. |
\(7~\mu \text{C}\) |
3. A neutral, isolated spherical copper particle of radius \(10~\text{nm}\) \((1~\text{nm}=10^{-9}~\text{m})\) is gradually charged by increasing the external voltage. The charging occurs slowly, such that electrons are added one at a time to the particle. Which of the following graphs correctly represents the variation of the total charge on the particle with the applied voltage?
4. Four resistors are connected as shown in the following figure. A
\(6\) V battery of negligible resistance is connected across terminals
\(A\) and
\(C.\) The potential difference across terminals
\(B\) and
\(D\) would be:

1. zero
2.
\(1.5\) V
3.
\(2\) V
4.
\(3\) V
5. A plane electromagnetic wave travels in a vacuum along the
\({z\text{-}}\)direction. Then the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors will be:
| 1. |
in the \({x\text{-}y}\) plane and they are parallel to each other. |
| 2. |
in the \({x\text{-}y}\) plane and they are mutually perpendicular to each other. |
| 3. |
in the \({y\text{-}z}\) plane and they are mutually perpendicular to each other. |
| 4. |
in the \({z\text{-}x}\) plane and they are parallel to each other. |
6. Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities
\(I\) and
\(4I\) superimpose. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are:
1. \(5I\) and \(I\)
2. \(5I\) and \(3I\)
3. \(3I\) and \(I\)
4. \(9I\) and \(I\)
7. The electric field vector of an electromagnetic wave is given by, \(\vec{E}=E_0 \sin (\omega t-k x) \hat{j}.\) The corresponding expression for magnetic field is:
1. \( \vec{B}=B_0 \sin (\omega t+k x) \hat{k} \)
2. \( \vec{B}=B_0 \sin (\omega t-k x) \hat{k} \)
3. \( \vec{B}=-B_0 \sin (\omega t+k x) \hat{k} \)
4. \( \vec{B}=-B_0 \sin (\omega t-k x) \hat{k}\)
8. The correct direction of the magnetic field in the given figures is shown by:
9. The current in an inductor of self-inductance \(4~\text{H}\) changes from \(4~ \text{A}\) to \(2~\text{A}\) in \(1~ \text s\). The emf induced in the coil is:
| 1. |
\(-2~\text{V}\) |
2. |
\(2~\text{V}\) |
| 3. |
\(-4~\text{V}\) |
4. |
\(8~\text{V}\) |
10. An ammeter of resistance \(20~\Omega\) measures up to \(50~\text{mA}.\) The value of shunt required in parallel to measure current up to \(5~\text A\) is nearly:
1. \( 0.1 ~\Omega \)
2. \( 0.2 ~\Omega \)
3. \( 0.02~ \Omega \)
4. \(0.01~ \Omega\)
11. Given below are two statements:
| Statement I: |
The reactance of an AC circuit is zero. It is possible that the circuit contains a capacitor and an inductor. |
| Statement II: |
In an AC circuit, the average power delivered by the source never becomes zero. |
| 1. |
Both Statement I and Statement II are True. |
| 2. |
Both Statement I and Statement II are False. |
| 3. |
Statement I is True but Statement II is False. |
| 4. |
Statement I is False but Statement II is True. |
12. The equivalent capacitance across \(A\) and \(B\) in the given figure is:

| 1. |
\( \dfrac{3}{2}C\) |
2. |
\({C}\) |
| 3. |
\( \dfrac{2}{3}{C}\) |
4. |
\( \dfrac{5}{3}C\) |
13. A conducting wire bent in the form of a parabola
\(y^{2}=2x\) carries a current
\(i=2~\text A\) as shown in the figure. The wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field
\(\vec B=-4\hat k ~\text{T}.\) The magnetic force on the wire is:
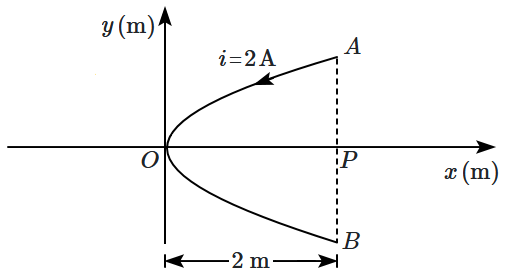
1.
\(-16\hat i~\text N\)
2.
\(32\hat i~\text N\)
3.
\(-32\hat i~\text N\)
4.
\(16\hat i~\text N\)
14. Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The magnetism of a magnet is due to the spin motion of electrons. |
| Reason (R): |
The dipole moment of an electron is smaller than that due to orbit motion around the nucleus. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
15. A hollow tube is carrying an electric current along its length distributed uniformly over its surface. The magnetic field,
| (a) |
increases linearly from the axis to the surface |
| (b) |
is constant inside the tube |
| (c) |
is zero at the axis |
| (d) |
is zero just outside the tube |
Choose the correct option:
| 1. |
(a), (b) |
2. |
(b), (c) |
| 3. |
(c), (d) |
4. |
(a), (d) |
16. What is the potential difference between points
\(A\) and
\(D\) of circuit shown in the figure?

1.
\(5~\text{V}\)
2.
\(9~\text{V}\)
3.
\(10.4~\text{V}\)
4.
\(11.4~\text{V}\)
17. There are certain materials developed in laboratories that have a negative refractive index (figure). A ray incident from the air (medium-\(1\)) into such a medium (medium-\(2\)) shall follow a path given by:
18. Magnetic flux through a circuit of resistance \(20~\Omega\) is changed from \(20\) Wb to \(40\) Wb in \(5\) ms. The charge passed through the circuit during this time is:
1. \(1\) C
2. \(2\) C
3. zero
4. \(0.5\) C
19. The figure shows some of the electric field lines corresponding to an electric field. The figure suggests that:

1. \(E_A>E_B>E_C\)
2. \(E_A=E_B=E_C\)
3. \(E_A=E_C>E_B\)
4. \(E_A=E_C<E_B\)
20. Light is:
| 1. |
a wave phenomenon |
| 2. |
a particle phenomenon |
| 3. |
both particle and wave phenomenon |
| 4. |
none of the above |
21. Two cells of the same emf \(E\) and different internal resistances \(r_1\) and \(r_2\) are connected in series to an external resistance \(R\). The value of \(R\) for which the potential difference across the first cell is zero is given by:

| 1. |
\(r_1\) |
2. |
\(r_2\) |
| 3. |
\(r_1-r_2\) |
4. |
\(r_1+r_2\) |
22. A convex lens made of glass has focal length \(0.15~\text m\) in air. If the refractive index of glass is \(3/2\) and that of water is \(4/3,\) the focal length of lens when immersed in water is:
1. \(0.45~\text m\)
2. \(0.15~\text m\)
3. \(0.30~\text m\)
4. \(0.6~\text m\)
23. The tangent at any point of an equipotential surface makes an angle \(\theta\) with the electric intensity vector at that point such that:
1. \(\theta=0^\circ\)
2. \(\theta=90^\circ\)
3. \(\theta=120^\circ\)
4. \(\theta=180^\circ\)
24. An infinite line charge produces a field of \(9\times10^{4}~\text{N/C}\) at a distance of \(2~\text{cm}\). The linear charge density is:
1. \(0.1~\mu\text{C/m}\)
2. \(100~\mu\text{C/m}\)
3. \(1.0~\mu\text{C/m}\)
4. \(10~\mu\text{C/m}\)
25. A rod of length \(l\) rotates with a uniform angular velocity \(\omega\) about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field \(B\) exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The potential difference between the two ends of the rod is:
1. zero
2. \(\frac{1}{2}Bl\omega ^{2}\)
3. \(Bl\omega ^{2}\)
4. \(2Bl\omega ^{2}\)
26. A dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of an isolated charged capacitor. Which of the following quantities will remain the same?
| (a) |
the electric field in the capacitor |
| (b) |
the charge on the capacitor |
| (c) |
the potential difference between the plates |
| (d) |
the stored energy in the capacitor |
Choose the correct option:
1. (a), (b)
2. (b) only
3. (c), (a)
4. (a), (d)
27. A ray is incident normally onto the surface
\(AB\) of the prism
\((\angle A=30^\circ,\angle B=90^\circ).\) The refractive index of the material of the prism is
\(\sqrt2.\) The deviation of this ray is:

1.
\(30^\circ\) downward
2.
\(15^\circ\) downward
3.
\(30^\circ\) upward
4.
\(15^\circ\) upward
28. Photons and electrons of the same wavelength are compared. Which one carries larger momentum?
| 1. |
photon |
| 2. |
electron |
| 3. |
neither, since both have equal momenta |
| 4. |
it could be either, depending on the energy |
29. A metallic resistor is connected across a battery. If the number of collisions of the free electrons with the lattice is somehow decreased in the resistor (for example, by cooling it), the current will:
| 1. |
increase |
2. |
decrease |
| 3. |
remain constant |
4. |
become zero |
30. Two concentric circular coils, one of small radius \({r_1}\) and the other of large radius \({r_2},\) such that \({r_1<<r_2},\) are placed co-axially with centres coinciding. The mutual inductance of the arrangement is:
1. \(\dfrac{\mu_0\pi r_1^2}{3r_2}\)
2. \(\dfrac{2\mu_0\pi r_1^2}{r_2}\)
3. \(\dfrac{\mu_0\pi r_1^2}{r_2}\)
4. \(\dfrac{\mu_0\pi r_1^2}{2r_2}\)
31. A transformer is used to light a \(100~\text{W}\) and \(110~\text{V}\) lamp from a \(220~\text{V}\) main. If the main current is \(0.5~\text{A},\) the efficiency of the transformer is approximately:
1. \(30\%\)
2. \(50\%\)
3. \(90\%\)
4. \(10\%\)
32. A Young's double-slit setup is first performed in air and then in a liquid of refractive index \(\mu.\) At a particular location on the screen, the \(10{\text{th}}\) bright fringe in air and the \(12\text{th}\) bright fringe in liquid coincide. Then \(\mu=\)
1. \(1.8\)
2. \(1.54\)
3. \(1.67\)
4. \(1.2\)
33. Consider the situation of the figure. The work done in taking a point charge from \(\mathrm{P}\) to \(\mathrm{A}\) is \(W_{\mathrm{A}}\) , from \(\mathrm{P}\) to \(\mathrm{B}\) is \(W_{\mathrm{B}}\) and from \(\mathrm{P}\) to \(\mathrm{C}\) is \(W_{\mathrm{C}}\). Then:

| 1. |
\(W_{\mathrm{A}}<W_{\mathrm{B}}<W_{\mathrm{C}}\) |
2. |
\(W_{\mathrm{A}}>W_{\mathrm{B}}>W_{\mathrm{C}}\) |
| 3. |
\(W_{\mathrm{A}}=W_{\mathrm{B}}=W_{\mathrm{C}}\) |
4. |
none of these |
34. Light travels in two media \(M_1\) and \(M_2\) with speeds \(1.5 \times 10^8 ~\text{ms}^{-1}\) and \(2.0 \times 10^8~ \text{ms}^{-1}\) respectively. The critical angle between them is:
1. \( \tan ^{-1}\left(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{7}}\right ) \)
2. \( \tan ^{-1}\left(\dfrac{2}{3}\right) \)
3. \(\cos ^{-1}\left(\dfrac{3}{4}\right) \)
4. \(\sin ^{-1}\left(\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\)
35. Two identical equilateral triangular prisms, each of which gives a minimum deviation of
\(60^{\circ}\) are taken: call these prisms
\(A,B\). These are placed as shown in the figure, and a ray of light is incident on prism
\(A\) at minimum deviation. Now prism
\(B\) is cut in half, along the dotted line, and the right half is removed. The deviation of the emerging ray is:

| 1. |
\(90^{\circ}\) |
2. |
\(45^{\circ}\) |
| 3. |
\(60^{\circ}\) |
4. |
\(30^{\circ}\) |
Physics - Section B
36. The threshold frequency of a photoelectric metal is
\(\nu_0.\) If the light of frequency
\(4\nu_0\) is incident on this metal, then the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons will be:
| 1. |
\(h\nu_0\) |
2. |
\(2h\nu_0\) |
| 3. |
\(3h\nu_0\) |
4. |
\(4h\nu_0\) |
37. The wavelength of the first spectral line of the Lyman series of the hydrogen spectrum is:
1. \(1218~\mathring A\)
2. \(974.3~\mathring A\)
3. \(2124~\mathring A\)
4. \(2120~\mathring A\)
38. The currents flowing through circuits
\(A\) and
\(B,\) respectively, are: (assume all diodes are ideal)
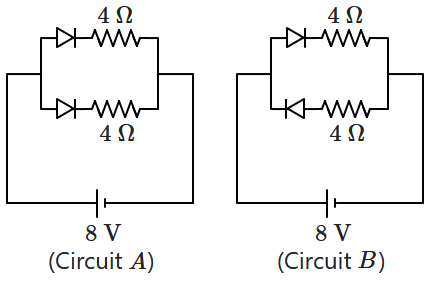
| 1. |
\(1\) A, \(2\) A |
2. |
\(2\) A, \(1\) A |
| 3. |
\(4\) A, \(2\) A |
4. |
\(2\) A, \(4\) A |
39. A \(\mathrm{p\text-n}\) junction has an electric field of \(6\times 10^{5}~\text{V/m}\) in the junction and the junction width is \(500~\text{nm}.\) The height of the potential barrier is:
1. \(0.6~\text V\)
2. \(0.3~\text V\)
3. \(0.5~\text V\)
4. \(0.25~\text V\)
40. Carbon, silicon, and germanium have four valence electrons each. These are characterized by valence and conduction bands separated by the energy bandgap respectively equal to \((E_g)_C, (E_g)_{Si}~\text{and}~(E_g)_{Ge}\). Which of the following statements is true?
| 1. |
\((E_g)_{Si} < (E_g)_{Ge}<(E_g)_{C}\) |
| 2. |
\((E_g)_{C} < (E_g)_{Ge}>(E_g)_{Si}\) |
| 3. |
\((E_g)_{C} > (E_g)_{Si}>(E_g)_{Ge}\) |
| 4. |
\((E_g)_{C} =(E_g)_{Si}=(E_g)_{Ge}\) |
41. Three ideal diodes are connected to the battery as shown in the circuit. The current supplied by the battery is:

1. zero
2. \(4~\text{A}\)
3. \(2~\text{A}\)
4. \(6~\text{A}\)
42. As per the given circuit, the value of current through the battery will be:

1.
\(4~\text{A}\)
2.
\(3~\text{A}\)
3.
\(2~\text{A}\)
1.
\(1~\text{A}\)
43. If the energy of the electron in an \(\mathrm{H}\)-atom in the ground state is taken to be \(-13.6\) eV, then the kinetic energy of the electron in the first excited state will be:
1. \(3.4\) eV
2. \(6.8\) eV
3. \(10.2\) eV
4. \(13.6\) eV
44. In a half-wave rectification, what is the output frequency if the input frequency is \(50~\text{Hz}?\)
1. \(50~\text{Hz}\)
2. \(100~\text{Hz}\)
3. \(25~\text{Hz}\)
4. \(60~\text{Hz}\)
45. A nucleus of mass number
\(189\) splits into two nuclei having mass numbers
\(125\) and
\(64.\) The ratio of the radius of two daughter nuclei respectively is:
| 1. |
\(25:16\) |
2. |
\(1:1\) |
| 3. |
\(4:5\) |
4. |
\(5:4\) |
46. Complex among the following that can exist as a pair of enantiomers is:
1. [Co(H2NCH2CH2NH2)3]3+
2. Trans-[Co(H2NCH2CH2NH2)2Cl2]+
3. [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
4. [Co{P(C2H5)3}2ClBr]
47. What amount of urea should be dissolved in 400 g of water to attain a solution with a
vapour pressure 2% lower than pure water?
1. 32.4 g
2. 27.2 g
3. 21.4 g
4. 24. 5 g
48.
| Assertion(A): |
1 M solution of KCl has greater osmotic pressure than 1 M solution of glucose at the same temperature |
| Reason(R): |
In solution, KCl dissociates to produce more number of particles |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are false |
49. Consider a zero-order reaction. The rate equation for the given expression \(2X + Y \rightarrow Z\) is:
1. Rate = \(k[X][Y]\)
2. Rate = \(k[X]^0[Y]^0\)
3. Rate = \(k[X]^0[Y]\)
4. Rate = \(k[X][Y]^0\)
50. Which of the following shows the least reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution reaction?
Chemistry - Section A
51. The major product of the following reaction is :
\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CHCO}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3 \xrightarrow{\mathrm{LiAlH}_4}\)
1.\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\)
2.\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
3.\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CHCH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\)
4.\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHO}\)
52. Choose the correct statement among the following about freons.
1. They are used as a cancer medicine.
2. They are chlorofluorocarbon compounds.
3. These are toxic organic compounds.
4. These are flammable compounds.
53. Match the complexes (given in column I) with their corresponding hybridisation (given in column II) and mark the appropriate choice.
|
Column I |
|
Column II |
| (A) |
\(\left[\mathrm{Ag}\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_2\right]^{+}\) |
(i) |
\(d^2 s p^3 \text {, octahedral }\) |
| (B) |
\(\left[\mathrm{Ni}(\mathrm{CN})_4\right]^{2-}\) |
(ii) |
\(d s p^2, \text { square planar }\) |
| (C) |
\(\left[\mathrm{Ni}(\mathrm{CO})_4\right]\) |
(iii) |
\(s p \text {, linear }\) |
| (D) |
\(\left[\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{CN})_6\right]^{3-}\) |
(iv) |
\(s p^3 \text {, tetrahedral }\) |
1. (A) → (i), (B) → (ii), (C) → (iii), (D) → (iv)
2. (A) → (iii), (B) → (ii), (C) → (iv), (D) → (i)
3. (A) → (iv), (B) → (iii), (C) → (ii), (D) → (i)
4. (A) → (ii), (B) → (i), (C) → (iii), (D) → (iv)
54. Electronic configuration of nickel in K2[NiCl4] is:
(Atomic number of Ni is 28)is:
1. \(e^3t^5_2 \)
2. \(e^3_gt^5_{2g} \)
3. \(e^3t^4_2 \)
4. \(e^4t^4_2 \)
55.
| Assertion (A): |
EDTA forms complex with divalent metals of 3d-series in the ratio of 1:1. |
| Reason (R): |
EDTA has \(4-\mathrm{COOH}\) groups. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
56.
| Assertion (A): |
Isopropyl chloride is more reactive than CH3Br in SN2 reactions. |
| Reason (R): |
SN2 reactions are always accompanied by inversion of configuration. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
(A) is False but (R) is True. |
57. In the electrolysis of dilute sulfuric acid employing a Platinum (Pt) electrode, the resulting product obtained at the anode would be:
1. Oxygen gas
2. gas
3. gas
4. Hydrogen gas
58.
The actinoid that can show oxidation states up to +7 is:
1. Am
2. Th
3. U
4. Np
59.
| Statement I: |
Ln oxides are used as phosphors in television screens and similar fluorescing surfaces. |
| Statement II: |
TiO is used in the pigment industry and MnO2 is used in dry battery cells. |
| 1. |
Only Statement I is correct. |
| 2. |
Only Statement II is correct. |
| 3. |
Both Statements I and II are correct. |
| 4. |
Both Statements I and II are false. |
60. The oxidation state of nickel in K
4[Ni(CN)
4] is:
61. The ratio of the number of electrons gained by acidified KMnO
4 and acidified K
2Cr
2O
7, respectively, in the given reaction is:
KMnO
4 \( \xrightarrow[]{H^{+}}\) Mn
2+
K
2Cr
2O
7 \( \xrightarrow[]{H^{+}}\) Cr
3+
| 1. |
5:6 |
2. |
6:5 |
| 3. |
3:5 |
4. |
5:3 |
62. One mole of propyl acetate on treatment with an excess of \(\mathrm{LiAlH}_4\) in dry diethyl ether followed by acidification gives:
1. 1 mole acetic acid + 1 mole ethyl alcohol
2. 1 mole ethyl alcohol + 1 mole methyl alcohol
3. 2 moles of ethyl alcohol
4. 1 mole of propyl alcohol + 1 mole of ethyl alcohol
63. Which of the following complex is/are homoleptic:
| a. |
\( {\left[\mathrm{Co}\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_6\right]^{3+}} \) |
b. |
\( {\left[\mathrm{Co}\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_5 \mathrm{Cl}\right]^{2+}} \) |
| c. |
\( {\left[\mathrm{Ni}(\mathrm{CN})_4\right]^{2-}}\) |
d. |
\(\left[\mathrm{Ni}\left(\mathrm{NH}_3\right)_4 \mathrm{Cl}_2\right]\) |
Choose the correct option.
1. (a, b)
2. (b, c)
3. (c, d)
4. (a, c)
64. Calculate the molarity of the KI solution, provided its density is 1.202 g mL-1 and it consists of a 20% (mass/mass) concentration.
1. 1.25 M
2. 1.95 M
3. 1.45 M
4. 2.15 M
65. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Acetic acid does not undergo haloform reaction. |
| Reason (R): |
Acetic acid has no alpha hydrogens. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are False. |
66. This reaction is a zero-order with respect to N
2O.
\({2 \mathrm{~N}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g})} \longrightarrow {2 \mathrm{~N}_2(\mathrm{~g})} \ + { \mathrm{~O}_2(\mathrm{~g})}\)
If the half-life for this reaction is 19.0 minutes and the initial concentration of N
2O is 1.39 M, then the value of rate constant k, is:
| 1. |
0.0158 mol L–1min–1 |
2. |
0.0263 mol L–1 min–1 |
| 3. |
0.0366 mol L–1 min–1 |
4. |
0.0526 mol L–1 min–1 |
67. Which of the following is classified as secondary benzylic alcohol?
68. Given that a certain electric current generates 0.504 grams of hydrogen in 2 hours. How many gram of mass of copper can be liberated by the same current when applied for the same duration in a solution of CuSO4?
1. 12.7
2. 16
3. 31.8
4. 63.5
69. Mixing 20 g of naphthoic acid \((C_{11}H_8O_2)\) with 50 grams of benzene results in a freezing point depression of 2K.\((K_f = 1.72 K ~kg ~mol^{-1}) \)
The Van't Hoff factor (i) is:
1. 0.5
2. 1
3. 2
4. 3
70. Match the column I with the column II and mark the appropriate choice.
|
Column I
(Process) |
|
Column II
(Reagent) |
| (A) |
Analytical chemistry |
(i) |
EDTA |
| (B) |
Volumetric estimation |
(ii) |
Silver complexes |
| (C) |
Catalyst |
(iii) |
\(\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}, \mathrm{Fe}^{3+}, \mathrm{Ni}^{2+}\) |
| (D) |
Electroplating |
(iv) |
\(\left(\mathrm{Ph}_3 \mathrm{P}\right)_3 \mathrm{RhCl}\) |
1. (A) → (ii), (B) → (iii), (C) → (i), (D) → (iv)
2. (A) → (i), (B) → (iii), (C) → (ii), (D) → (iv)
3. (A) → (iii), (B) → (i), (C) → (iv), (D) → (ii)
4. (A) → (i), (B) → (iv), (C) → (ii), (D) → (iii)
71. The equilibrium constant value for the given reaction is:
Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
(Given: EƟ(cell) = 0.46 V)
1. 3.92 × 1014
2. 3.92 × 1015
3. 3.92 × 1016
4. 3.92 × 1017
72. The structure of A and B respectively in the following reaction is:

73. Identify X in the following sequence of reactions :
\(\mathrm{X} \xrightarrow[\text { (ii) } \mathrm{H}^{+} / \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}]{\text { (i) } \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{MgX}} \mathrm{C}_5 \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O} \xrightarrow[573 \mathrm{~K}]{\mathrm{Cu}} \mathrm{C}_5 \mathrm{H}_{10}\)
| 1. |
\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COCH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\) |
| 2. |
\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHO}\) |
| 3. |
\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHO}\) |
| 4. |
\(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\) |
74. The following reaction is first order,
\(A(g)\longrightarrow~B(g)+C(g) \)
Given that the initial pressure of A is 100 torr and the total pressure of the mixture is increased by 50 torr in 8 min. Calculate the half-life of the reaction.
1. 4 min
2. 8 min
3. 16 min
4. 32 min
75. Which of the following reactions is correct?
76. Which of the following compounds can yield only one monochlorinated product upon free radical chlorination?
1. 2, 2‐Dimethylpropane
2. 2‐Methylpropane
3. 2‐Methylbutane
4. n‐Butane
77. The IUPAC name for the following compound is:

| 1. |
4-Hexen-3-one |
2. |
3-Hexenone |
| 3. |
2-Hexene-4-one |
4. |
Hex-3-on-4-ene |
78. The correct cell representation for the reaction given below is:
\(\mathrm{H}_2+2 \mathrm{AgCl} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}^{+}+2 \mathrm{Ag}+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \)
1. \(\mathrm{Pt}\left|\mathrm{H}_2\right| \mathrm{HCl}|| \mathrm{AgCl} \mid \mathrm{Ag} \)
2. \(\mathrm{Pt}\left|\mathrm{H}_2\right| \mathrm{HCl}|| \mathrm{AgCl} \mid \mathrm{Pt} \)
3. \(\mathrm{Ag}|\mathrm{AgCl}| \mathrm{HCl}\left|\mathrm{H}_2\right| \mathrm{Pt} \)
4. \(\mathrm{Pt}|\mathrm{AgCl}| \mathrm{HC}|| \mathrm{H}_2 \mid \mathrm{Pt} \)
79. IUPAC name of the following compound is:
1. 1-Methoxy-1-methylethane
2. 2-Methoxy-2-methylethane
3. 2-Methoxypropane
4. Isopropylmethyl ether
80. The following reaction is given for reference.

'A' (Major product) is:
81. Identify the compound that on Aldol condensation followed by dehydration gives methyl vinyl ketone.
1. Methanal and ethanal
2. Two moles of formaldehyde
3. Methanal and propanone
4. Two moles of ethanal
82. The product yield from the reaction of a ketone and amine is:
1. Amides
2. Oximes
3. Urea
4. Imines
83. Which one of the following bases is not present in DNA?
1. Quinoline
2. Adenine
3. Cystosine
4. Thymine
84. The correct statement(s) among the following is or are:
| I: |
Cr2+ and Mn3+ have the same electronic configuration. |
| II: |
Cr2+ is a reducing agent, while Mn3+ is an oxidising agent. |
| III: |
Cr2+ is an oxidising agent, while Mn3+ is a reducing agent. |
| IV: |
Both Cr and Mn are oxidising agents. |
1. I,III,IV
2. I,II
3. I,II,IV
4. I,IV
85. Which of the following hormones contains iodine?
1. Insulin
2. Testosterone
3. Adrenaline
4. Thyroxine
Chemistry - Section B
86. α-helix structure of proteins is stabilized by :
| 1. |
H-bonds formed between the −SH and C=O group. |
| 2. |
H-bonds formed between the −NH and C=O group. |
| 3. |
Ionic bonds formed between the −SH and C=O group. |
| 4. |
Ionic bonds formed between the −NH and C=O group. |
87. The amine that reacts with Hinsberg's reagent to give an alkali insoluble product is:-
88. Which of the following is more basic than aniline?
1. Diphenylamine
2. Triphenylamine
3. p-nitroaniline
4. Benzylamine
89. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Boron is the hardest element in group 13. |
| Reason (R): |
High lattice enthalpy is due to the strong crystalline lattice. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. |
(A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. |
Both (A) and (R) are false |
90. For an ideal solution, the correct option is:
1. at constant T and P
2. at constant T and P
3. at constant T and P
4. at constant T and P
91. 'Heat shock' method in bacterial transformation:
| 1. |
allows selection of transformants |
| 2. |
promotes uptake of DNA through membrane transport proteins |
| 3. |
creates pores in the bacterial plasma membrane and allows plasmid
DNA to enter the bacterial DNA. |
| 4. |
coagulates DNA in the bacterial cell. |
92. Rate of decomposition of detritus is expected to be highest in which of the following ecosystem?
1. Tropical rain forest
2. Antarctic
3. Dry arid region
4. Alpine region
93. If an anther is to stamen, similarly an embryo sac is to:
| 1. |
Microspore |
2. |
Ovule |
| 3. |
Ovary |
4. |
Gynoecium |
94. Mycorrhiza help the host plant in:
| I: |
Enhancing its phosphorus uptake capacity |
| II: |
Increasing its tolerance to drought |
| III: |
Enhancing its resistance to root pathogens |
1. Only
I and
II
2. Only
I and
III
3. Only
II and
III
4.
I,
II and
III
95. Genes assort independently if they are situated on the:
1. heterologous chromosomes
2. homologous chromosomes
3. extra nuclear genetic element
4. same chromosome
96. The sobriquet ‘lungs of the planet Earth’ is sometimes used for:
1. Taiga forest
2. Tundra forest
3. Amazon rain forest
4. Rain forests of North East India
97. AUG codon:
a. codes for methionine
b. is an initiation codon
1. Only a is correct
2. Only b is correct
3. Both a and b are correct
4. Both a and b are incorrect
98. PCR (polymerase chain reactions) became available for routine use in molecular diagnosis due to:
1. Easy availability of DNA template
2. Availability of synthetic primers
3. Availability of cheap deoxyribonucleotides
4. Availability of 'Thermostable' DNA polymerase
99. On average, only about what percent of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level?
1. 1%
2. 10%
3. 40%
4. 90%
100. Which Indian plant is the source of antihypertensive drug reserpine?
1. Datura
2. Rauwolfia
3. Atropa
4. Papaver
Biology I - Section A
101. The technology of biogas production from cow dung was developed in India largely due to the efforts of:
| 1. |
Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited |
| 2. |
Oil and Natural Gas Commission |
| 3. |
Indian Agricultural Research Institute and Khadi & Village Industries Commission |
| 4. |
Indian Oil Corporation. |
102. The large holes in Swiss cheese are made by a:
| 1. |
a unicellular fungus |
| 2. |
a bacterium that produces methane gas |
| 3. |
a bacterium producing a large amount of carbon dioxide |
| 4. |
a fungus that releases a lot of gases during its metabolic activities. |
103. Biodiversity hot spots are characterised by:
| I: |
Large number of species |
| II: |
Abundance of endemic species |
| III: |
Low threat of extinction |
1. Only
I and
II are correct
2. Only
I and
III are correct
3. Only
II and
III are correct
4.
I,
II and
III are correct
104. Which of the following is used to estimate the biochemical oxygen demand and hence the polluting potential of a sample of water?
1. total organic matter
2. biodegradable organic matter
3. oxygen evolution
4. oxygen consumption
105. In an ecosystem, all the following organisms can be producers except:
1. Spirogyra
2. Agaricus
3. Volvox
4. Nostoc
106. Identify the incorrect statements regarding a typical embryo sac of a flowering plant:
| I: |
It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity |
| II: |
It is free-nuclear during the development |
| III: |
It is situated inside the integument but outside the nucellus |
| IV: |
It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end |
1.
I and
IV
2.
II and
III
3.
I and
II
4.
III and
IV
107. How many of the given pairs are correctly matched?
| I: |
Lady birds: Aphids |
| II: |
Dragon fly: Mosquito |
| III: |
Trichoderma: Fungicide |
1. 0
2. 1
3. 2
4. 3
108. Where can you find an inverted ecological pyramid of biomass?
1. Forest ecosystem
2. Marine ecosystem
3. Grass land ecosystem
4. Desert ecosystem
109. In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA molecules are separated on the basis of their:
1. Charge only
2. Size only
3. Charge to size ratio
4. All of the above
110. Retroviruses:
| I: |
contain ssRNA as their genetic material. |
| II: |
have the presence of reverse transcriptase, an enzyme that transcribes RNA into DNA. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
111. Golden rice is a transgenic rice having gene for production of:
1. Erythropoietin
2. β – carotene
3. Thymosin
4. ADA
112. A type of asexual reproduction in plants where seeds are produced without the process of fertilization is called as:
1. Parthenocarpy
2. Apomixis
3. Vegetative propagation
4. Sexual reproduction.
113. Which enzyme must not be used when isolating DNA in pure form from a bacterial cell?
1. Lysozyme
2. Ribonuclease
3. Deoxyribonuclease
4. Protease
114. Deoxyribose and ribose are monosaccharides and:
1. trioses
2. hexoses
3. pentoses
4. polysaccharides
115. In a dihybrid cross involving two genes [assume independent assortment], the F1 heterozygote [AaBb] is crossed with homozygous recessive parental pea (aa bb). What would be the ratio of offspring in the next generation?
| 1. |
1 : 1 : 1: 1 |
2. |
9 : 3 : 3 : 1 |
| 3. |
3 : 1 |
4. |
1 : 1 |
116. Only xenogamy is possible in:
1. Monoecious plant bearing unisexual flowers
2. Dioecious plant bearing only male or female flowers
3. Monoecious plant with bisexual flowers
4. Dioecious plant with bisexual flowers
117. Which cells undergo meiosis during microsporogenesis?
1. Tapetum cells
2. Microspore mother cells
3. Microspores
4. Pollen grains.
118. 'Restriction' in Restriction enzyme refers to:
| 1. |
Cleaving of phosphodiester bond in DNA by the enzyme |
| 2. |
Cutting of DNA at specific position only |
| 3. |
Prevention of the multiplication of bacteriophage by the host bacteria |
| 4. |
All of the above |
119. Study the given two statements regarding the process of decomposition in an ecosystem:
| I: |
By the process of leaching, water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts. |
| II: |
Bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. This process is called catabolism. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
120. In the mature mRNA in eukaryotes:
1. exons and introns do not appear
2. exons appear but introns do not appear
3. introns appear but exons do not appear
4. both exons and introns appear
121. If a dicot plant bears flowers but never produces fruits and seeds, the plant is most likely:
1. Dioecious with only pistillate flowers
2. Dioecious with only staminate flowers
3. Plant is monoecious
4. Plant is self-pollinated
122. Cry proteins are produced by Bacillus thuringiensis as protoxin which is:
1. A non-pathogenic but active toxin
2. A denatured toxin
3. A toxin produced by a probiotic bacteria
4. An Inactive precursor of a toxin
123. A plant producing light, non-sticky pollen in large numbers and with long and feathery stigmas is most likely pollinated by:
| 1. |
Insects |
2. |
Water |
| 3. |
Wind |
4. |
Animals |
124. Which cells of an embryo sac degenerate after fertilisation?
1. Synergids and primary endosperm cell
2. Synergids and antipodals
3. Antipodals and primary endosperm cell
4. Egg and antipodals.
125. In RNAi is a type of post-transcriptional gene silencing with the help of:
| 1. |
ss DNA |
2. |
ds DNA |
| 3. |
ds RNA |
4. |
ss RNA |
126. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The number of trophic levels in the grazing food chain is restricted. |
| Reason (R): |
A grazing food chain (GFC) is a type of food chain where energy is acquired through photosynthesis. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
127. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Incomplete dominance and blending inheritance are synonymous. |
| Reason (R): |
The phenotype of the heterozygous genotype is distinct from and often
intermediate to the phenotypes of the homozygous genotypes. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
128. Consider the given two statements:
| Statement I: |
Both wind and water pollinated flowers are not very colourful and do not produce nectar. |
| Statement II: |
Majority of insect-pollinated flowers are large, colourful, fragrant and rich in nectar. |
1. Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct
2. Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct
3. Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect
4. Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is incorrect
129. Consider the given two statements:
| Statement I: |
VNTR belongs to a class of satellite DNA referred to as mini-satellite. |
| Statement II: |
VNTR do not show polymorphism. |
| 1. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct |
| 2. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct |
| 3. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect |
| 4. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is incorrect |
130. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The most common type of embryo sac development in angiosperms is the Polygonum type or the Monosporic type. |
| Reason (R): |
This type of development is characterized by the formation of a seven-celled, eight-nucleate embryo sac. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
131. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Geitonogamy does not provide the same advantages as cross-pollination. |
| Reason (R): |
Geitonogamy is a type of pollination in plants where pollen is transferred from the anther of a flower to the stigma of another flower on the same plant. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
132. Consider the given two statements:
| Statement I: |
In predation, parasitism and commensalism, the interacting species live closely together. |
| Statement II: |
In predation, parasitism and commensalism, one of the interacting species benefits and the other suffers harm. |
| 1. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct |
| 2. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct |
| 3. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect |
| 4. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is incorrect |
133. Consider the given two statements:
| Statement I: |
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process that regulates gene expression. |
| Statement II: |
RNAi takes place only in plants as a method of cellular defense. |
| 1. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is correct |
| 2. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct |
| 3. |
Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect |
| 4. |
Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is incorrect |
134. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The indiscriminate use of chemical pesticides is not desirable |
| Reason (R): |
Chemical pesticides are non-specific, toxic and harmful. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
135. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Of the two nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, only DNA can act as genetic material |
| Reason (R): |
Only DNA and not RNA has the capability to generate its replica. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is False |
Biology I - Section B
136. What is the urethral meatus?
| 1. |
The point of entry of urethra into the prostate gland |
| 2. |
Opening of ejaculatory duct into urethra |
| 3. |
External opening of the urethra |
| 4. |
Muscles surrounding the urethra |
137. More the distance between the genes on a chromosome:
| 1. |
more is the percent of recombinants formed on a test cross |
| 2. |
less is the percent of recombinants formed on a test cross |
| 3. |
more is the percent of recombinants formed on a test cross if the distance is more than 10 map units but less than 15 map units |
| 4. |
more is the percent of recombinants formed on a test cross if the distance is more than 5 map units but less than 10 map units |
138. In order to produce a recombinant protein in large amounts, the best strategy is to use:
1. A batch culture
2. A stirred-tank bioreactor without in-lets and out-lets
3. A continuous culture system
4. Lab flask culture
139. Which of the following animals called evolved into the first amphibians that lived on both land and water?
1. Lobe fish
2. Cynagnathous
3. Seymouria
4. Megalodon
140. Identify the scientist known for his discovery of recombinant DNA, or gene splicing technology?
| 1. |
Herbert Boyer |
2. |
Hargobind Khurana |
| 3. |
Kary Mullis |
4. |
Arthur Kornberg |
141. Regarding rheumatoid arthritis:
| I: |
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder. |
| II: |
In rheumatoid arthritis, the body's immune system attacks its own tissue, including joints. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
142. What conditions of the primeval earth, as proposed by Oparin, were simulated in his experiment by S. L. Miller in 1953?
| 1. |
low temperature, volcanic storms, atmosphere rich in oxygen |
| 2. |
low temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere |
| 3. |
high temperature, volcanic storms, non-reducing atmosphere |
| 4. |
high temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere containing CH4, NH3 etc. |
143. Mutated genes that can cause cancer are called:
1. structural genes
2. expressor genes
3. oncogenes
4. regulatory genes
144. After receiving the duct from the seminal vesicle, vas deferens opens into urethra as:
1. Epididymis
2. Ejaculatory duct
3. Efferent ductule
4. Ureter
145. Which laboratory test is usually employed to confirm the diagnosis of typhoid fever?
1. Haemogram
2. ESR
3. PCR
4. Widal
146. Which class of antibodies present in colostrum provides new born with passive immunity?
1. Ig G type
2. Ig A type
3. Ig D type
4. Ig E type
147. The bones of forelimbs of different mammals like whale, bat, cheetah and man are remarkably similar in structure, because:
| 1. |
these mammals have undergone convergent evolution |
| 2. |
they share a common ancestor |
| 3. |
they perform the same function |
| 4. |
random chance mutations led to development of bones in different groups |
148. Regarding IUDs:
a: They are effective contraceptives
b: IUDs increase phagocytosis reaction in the uterus
c: IUDs suppress gametogenesis
d: IUDs once inserted need not be replaced
1. Only a and b are correct
2. Only c and d are correct
3. Only a and c are correct
4. Only b and d are correct
149. Which endocrine gland is important for the development of acquired immunity in human beings?
1. Pineal
2. Pituitary
3. Thymus
4. Thyroid
150. If IMR [Infant Mortality Rate] and MMR [Maternal Mortality rate] in a population are decreased, the population will most likely show:
1. an increase in growth rate
2. a decline in growth rate
3. a negative growth rate
4. no change in growth rate
Biology II - Section A
151. Symptoms indicative of pneumonia include:
| 1. |
Difficulty in respiration, fever, chills, cough, headache |
| 2. |
Constipation, abdominal pain, cramps, blood clots |
| 3. |
Nasal congestion and discharge, cough, constipation, headache |
| 4. |
High fever, weakness, stomach pain, loss of appetite and constipation |
152. Organs that have different anatomical structures but similar functions are the result of:
1. divergent evolution
2. artificial selection
3. genetic drift
4. convergent evolution
153. A changed chromosome number such as 2n +1, 2n –1 and 2n + 2, 2n – 2 is called:
1. Aneuploidy
2. Polyploidy
3. Allopolyploidy
4. Monosomy
154. At what stage of the embryonic development does implantation take place?
1. Morula
2. Zygote
3. Blastocyst
4. Gastrula
155. India began implementing a Family Welfare Program in:
1. 1950s
2. 1960s
3. 1980s
4. 1990s
156. The process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits is:
1. reverse evolution
2. artificial selection
3. mutation
4. natural selection
157. α -1 antitrypsin:
| I: |
is a n enzyme |
| II: |
is used to treat certain cases of pneumonia |
| 1. |
Only I is correct |
| 2. |
Only II is correct |
| 3. |
Both I and II are correct |
| 4. |
Both I and II are incorrect |
158. The complementary base pairing ensure which of the following features of a DNA double helix?
| 1. |
the antiparallel nature |
2. |
the semiconservative nature |
| 3. |
uniform diameter |
4. |
uniform length |
159. What type of selection was operative in industrial melanism observed in peppered moth, Biston betularia?
1. Stabilising
2. Directional
3. Disruptive
4. Artificial
160. Graft rejection by recipient body in transplantation surgery is due to:
1. auto-immune response
2. humoral immune response
3. physiological immune response
4. cell-mediated immune response
161. Z Z / ZW, female heterogamety, type of sex determination is seen in:
1. Platypus
2. Snails
3. Cockroach
4. Fowl
162. Which step of PCR reaction is carried out at a high temperature of about 98 degree celsius?
1. Denaturation of template DNA
2. Annealing of primers to template DNA
3. Extension of primer end on the template DNA
4. Both II and III
163. Identify the incorrect statement from the following:
| a: |
High levels of estrogen triggers the ovulatory surge. |
| b: |
Oogonial cells start to proliferate and give rise to functional ova in regular cycles from puberty onwards. |
| c: |
Sperms released from seminiferous tubules are highly motile. |
| d: |
Progesterone level is high during the post ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle |
1. Only
a,
b and
c
2. Only
a,
c and
d
3. Only
b,
c and
d
4.
a,
b,
c and
d
164. Identify the period during which a mature Graafian follicle is expected to be found in the ovary of a healthy human female?
1. 5 – 8 day of menstrual cycle
2. 11 – 14 day of menstrual cycle
3. 18 – 23 day of menstrual cycle
4. 24 – 28 day of menstrual cycle
165. Diaphragms, contraceptive devices used by the females, are
| I: |
introduced into the uterus |
| II: |
placed to cover the cervical region |
| III: |
act as physical barriers for sperm entry |
| IV: |
act as spermicidal agents |
| 1. |
Only I and II are correct |
| 2. |
Only I and III are correct |
| 3. |
Only II and III are correct |
| 4. |
Only III & IV are correct |
166. What, most likely, would be the mode of inheritance if a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny?
| 1. |
Autosomal dominant |
2. |
Autosomal recessive |
| 3. |
Sex-linked dominant |
4. |
Sex-linked recessive |
167. Sickle cell anaemia:
| a: |
can be treated with iron supplements |
| b: |
is a molecular disease |
| c: |
confers resistance to acquiring malaria |
1. Only
a and
b are correct
2. Only
a and
c are correct
3. Only
b and
c are correct
4.
a,
b, and
c are correct
168. Which part of the human sperm has a large number of mitochondria essential for sperm motility?
1. Head
2. Middle piece
3. Acrosome
4. Tail
169. At the time of ovulation, the secondary occyte is covered by a glycoprotein layer termed as:
1. Corona radiata
2. Zona radiata
3. Zona pellucida
4. Chorion
170. The process of DNA uptake by the bacteria from the surrounding environment is called:
1. Transformation
2. Transduction
3. Conjugation
4. Transfection
171. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
Personal protection like wearing face masks and repeated hand washing are important to limit the spread of diseases like Covid 19. |
| Reason (R): |
Diseases like Covid 19 spread mainly through droplet and articles used by infected person. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
172. How many of the given genetic disorders are inherited as a recessive condition?
I: Sickle cell anaemia
II: Colour blindness
III: Phenylketonuria
IV: Haemophilia
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. 4
173. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The lac operon will not be transcribed if lactose is absent. |
| Reason (R): |
Lactose is the inducer of the lac operon. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
174. During gametogenesis, which of the following are formed after Meiosis II?
I: Spermatids
II: Ovum
III: First polar body
1. Only I and II
2. Only I and III
3. Only II and III
4. I, II and III
175. Regarding LH [luteinizing hormone]:
| I: |
An LH surge triggers ovulation. |
| II: |
LH stimulates Leydig cells to secrete androgens. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
176. The number of correct statements from the given statements is:
| I: |
Ramapithecus was more man-like, while Dryopithecus was more ape-like. |
| II: |
Homo habilis had a brain capacity between 650-800cc. |
| III: |
Homo erectus probably did not eat meat. |
| IV: |
Agriculture came around 10,000 years ago, and human settlements started. |
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. 4
177. How many of the given statements regarding menstrual cycle are correct?
| I: |
The reproductive cycle in the female primates is called menstrual cycle. |
| II: |
The first menstruation begins at puberty and is called menarche. |
| III: |
Normally, one ovum is released (ovulation) during the middle of each menstrual cycle. |
| IV: |
The cycle starts with the menstrual phase. |
| V: |
In human beings, menstrual cycle ceases at around 50 years of age; that is termed as menopause. |
1. 2
2. 3
3. 4
4. 5
178. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
The use of natural methods for contraception involves almost nil side effects. |
| Reason (R): |
Natural methods work on the principle of avoiding chances of ovum and sperms meeting. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
179. Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): |
tRNA is the adapter molecule in the flow of genetic information in a typical cell. |
| Reason (R): |
tRNA has some unusual bases present in the sequence of its nucleotides. |
| 1. |
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) correctly explains (A) |
| 2. |
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not correctly explain (A) |
| 3. |
(A) is True, (R) is False |
| 4. |
(A) is False, (R) is True |
180. According to The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2017:
| I: |
a pregnancy may be terminated on certain considered grounds within the first 12 weeks of pregnancy on the opinion of one registered medical practitioner. |
| II: |
if the pregnancy has lasted more than 12 weeks, but fewer than 24 weeks, two registered medical practitioners must be of the opinion, formed in good faith, that the required ground exists. |
1. Only
I is correct
2. Only
II is correct
3. Both
I and
II are correct
4. Both
I and
II are incorrect
*If above link doesn't work, please go to test link from where you got the pdf and fill OMR from there
CLICK HERE to get FREE ACCESS for 2 days of ANY NEETprep course














































